Abstraction:
Abstraction is important as it can make complex problems easier to understand, making it easier and faster to solve with simpler solutions. Here is an example of abstraction: link to physics simulation
Representational abstraction:
- Removing unnecessary details to represent a problem using its key features, only relevent information kept.
Data Abstraction:
- Details about how data is being stored is hidden. For example, I know how to make a javascript array but I don't know how it works internally.
Abstraction by Generalisation:
- Grouping together similarities within a problem to identify the kind of problem.
- A common solution can be used to solve these problems
Thinking Ahead
Thinking ahead is the process of planning how a problem will be solved before writing code, focusing on inputs, outputs, preconditions, and caching:
- Inputs include any data required to solve the problem
- Outputs are the results that are passed back
- Data types and structures should be considered
- Preconditions are requirements which must be met before a program can be executed
- Commonly used function can be packaged into libraries for reuse. These are more reliable that newly-coded components as they have been tested, and it saves time
- Caching is storing data in a temporary memory location to avoid repeating expensive or time-consuming operations.
Thinking Procedurally
Procedural Abstraction
- Using a procedure to carry out a sequence of steps to achieve a task. The programmer doesn't need to understand the code itself, they just need to know the order of the procedures, the arguments required, and the data types included.
Problem decomposition
- This breaks a large, complex problem down into smaller subproblems which can be solved more easily
- Top-down design is breaking down the task until each subproblem is a single task which can be solved using a single subroutine. Each subroutine is self-contained
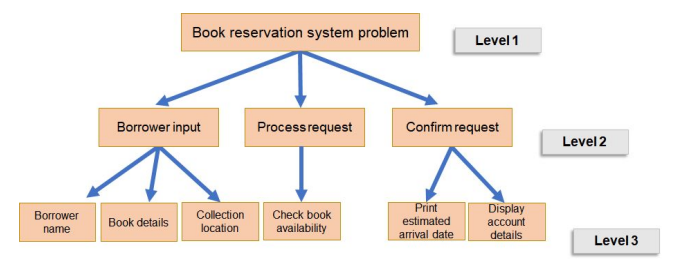
Thinking Logically
The structured approach
This approach aims to improve the clarity and maintainability of programs, only using three programming strucutures.
- Sequence - one statement following another
- Selection - if, else ... statements
- Iteration - while, for ... statements
Tools for designing algorithms
Flow diagrams and pseudocode are commonly used for designing algorithms.
An example:
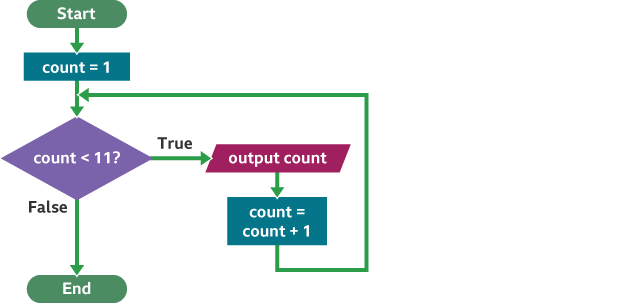
Thinking concurrently
Parallel computing
Multiple processors each executing different instructions simultaneously, aiming to speed up computations
Advantages and disadvantages:
- Speed up processing repetitive caluclations which need to be performed on large amounts of data
- Graphic processors can quickly render a 3D image
- Processors need to be coordinated so some tasks may run faster with a single processor
Concurrent processing
Single processor running several processes, each in turn being given a slice of processor time. This makes it look as though they are performed simultaneously.
Advantages and disadvantages:
- Increased program throughput
- Wasted time could be spent on another task
- If a large number of users try to run lots of computationally heavy programs, they will take longer to complete
Computable problems
A problem is computable if there is an algorithm which can solve it in a finite number of steps, in a reasonable amount of time.
Methods and strategies of problem solving
- Enumeration - an exhaustive search listing all cases. This is inefficient.
- Simulation - designing a model of a real system to the behaviour of the system. Uses abstraction when making the model.
- Divide and conquer - reduces size of the problem with every iteration
- Abstraction - remove details to simplify problem
Problem solving
Visualisation
How a problem is presented is a very important factor in finding a solution.
Backtracking
Visiting each path and building a solution based on the paths found to be correct. An example of this is the depth-first graph traversal
Data mining
Identifying patterns, correlations/connections, outliers, or future trends in large sets of data , big data. Big data is the term used for large sets of data that cannot easily be handled in a traditional database
Intractable problems
Problem which an algorithm may exist for its solution but would take an unreasonably long time to find.
Heuristic Methods
Heuristics are a non-optimal approach used to find approximate solutions to a problem, which can be done in a reasonable time frame. Solutions found are not perfectly accurate or complete.
Performance modelling
Estimates how a system will perform under different conditions, using mathematical methods, as it may be expensive or difficult to test properly.
Pipelining
Splitting of tasks into smaller parts and overlapping the processing of each part of the task. Used in FDE cycle which can be demonstrated here: Amazing website.


